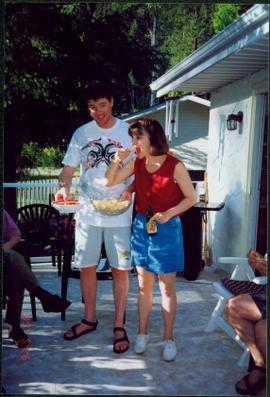Photograph depicts Judy Kennedy holding Prince George Arts Gallery of Honour Trophy. Judy accepted the award on behalf of Bridget Moran. Hallway wall and door in background.
Audio recording consists of an interview by Bridget Moran with James McCallum recalling his life, first in Scotland, then Montana and then as a wheat farmer in Success, Saskatchewan. McCallum (1891-1983) served on several community organizations including delegate of the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool (1938-1944) and director (1944-63). James McCallum died January 9, 1983 in Swift Current, Saskatchewan age 91.
Audiocassette Summary
- Recalls Success neighbours; Frazer [sp?] a family immigrated from Russia
- Recalls father dying at age 96
- James and his wife Sadie moved into the elder McCallum family homestead in 1962
- Recalls first date with wife in 1912 at dance; famous storm same night killed people in Regina
- Recalls playing violin at dances with Jack Pickett
- Bridget asks his memories of the Drugan family [Bridget’s; James recalls when his wife Sadie and Bridget’s mother became friends. Bridget used to stay with Sadie’s mother.
- Recalls medical facilities in early years; recalls father having blood poisoning and being attended by [the elder] Dr. Graham
End of tape
Audio recording consists of an interview by Bridget Moran with James McCallum recalling his life, first in Scotland, then Montana and then as a wheat farmer in Success, Saskatchewan. McCallum (1891-1983) served on several community organizations including delegate of the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool (1938-1944) and director (1944-63). James McCallum died January 9, 1983 in Swift Current, Saskatchewan age 91.
Audiocassette Summary
- McCallum family moved from rural Scotland to Montana and later Success, Saskatchewan. James McCallum born in Scotland – Nov 12, 1891
- James’ family left Scotland c.1899 via the ship “Caledonia” and came to Montana
- In 1904 his father decided to move the family
- Recalls living in Montana
- Recalls night at the Shaw farm in Montana with horse thieves the night his brother Allan was born
- Discusses trek to Saskatchewan arriving first in Swift Current, Saskatchewan;
- Homesteaded in Success [District], Saskatchewan
- Family’s land was Government land
- Moved from homestead to another farm
- Recalls his schooling; public school in Scotland; private school in Canada
- Talks about ranching
- Discusses income of family
- Describes types of farm machinery and combines; walking plow
- Talks about boundaries for land – no fences etc.
- Provides memories of families from the community
- Recalls memories of his mother managing household on farm
- Recalls work with threshing groups
- Recalls beginning of the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool to ensure farmers received fair payment for sale of their wheat
- Recalls attending meetings as delegate for the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool at the Canadian Federation of Agriculture; meetings held in various locales from Montreal to Vancouver
End of tape
Photograph depicts two buildings behind fence, sheds visible in background. Unidentified men can be seen walking in foreground. Small structures believed to be teepees can be seen behind fence.
Audio recording is of an interview by Bridget Moran with both Mr. George Henry and Mr. Arnold Davis to discuss their memories of the early town site development of South Fort George and Central Fort George c.1910-c.1917. Mr. Henry was born in 1882 and his family arrived in Quesnel in 1909. Mr. Henry’s interview is primarily about his work as a captain on the BX Sternwheeler up until the time of the railroad arriving in Prince George in 1914. Mr. Davis, who was a Sherriff in Prince George, recalls his childhood memories of Fort George and Central Fort George c.1917. Mr. Davis also discusses his family roots from Ireland, the family’s arrival in Fort George from Ashcroft in 1917 and memories of his father who worked on the sternwheelers on the Fraser River.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content:
Interview with Mr. George Henry
Mr. Henry was born in 1882 in Northern California and his family came to the Cariboo in 1909. He recalls riding his bicycle from Ashcroft to Quesnel in 3 days to find work with the BC Express Company.
Mr. Henry recalls working on the BX and describes the sternwheeler trip from Quesnel to South Fort George; it was a 3 hour trip from Quesnel and included two mail stops ;
Henry recalls an accident onboard the sternwheeler going through the Fraser Canyon (see p.p.11-12 of
Prince George Remembered)
Mr. Henry describes his homestead at South Fort George
Mr. Henry describes the BX sternwheeler being aground at South Fort George c.1920
Mr. Henry recalls spending winters in South Fort George in his log cabin; that work was “plentiful” in 1910 and the population at “about 700”
Mr. Henry notes that the “Indian reserve was at the Hudson’s Bay company” and that the native population was at “about 50”
Mr. Henry recalls the early commercial businesses in South Fort George c.1910 including the Northern Hotel; the candy store and ice cream store and theatre.
Mr. Henry describes the start of the town site of Central Fort George as a “viable little town” which started once the Grand Trunk Railway arrived and recalls the change in population between South Fort George & Central Fort George.
Henry recalls how all the workers came and lived in tents in Central Fort George.
Mr. Henry was not happy about the arrival of the railway as it meant he lost his job on the sternwheeler – he recalls that “us old river rats were just lost” (see p.p.34 of Prince George Remembered)
Bridget then asks Mr. Arnold Davis to recall his memories of early South Fort George
But first asks him to describe his family’s roots (See p.p. 1-2 of Prince George Remembered)
Scope and Content:
Interview with Mr. Arnold Davis
Davis notes he is 6th generation Canadian; family came from Ireland and his grandfather’s brother Jeff Davis became the President of the Confederate States of America.
Davis refers to his mother’s family being on the Prairies at time of the trial of Louis Riel
Davis explains that his grandfather first homesteaded at Banff; then Kamloops; then Ashcroft and on to South Fort George in 1917.
Davis’ father worked for the BC Express Company and he recalls being on the sternwheeler as a child during same time that George Henry worked the boats. Recalls workers on the boat; eating pie on the boat baked by the Chinese cook; (See p. 33 of Prince George Remembered)
Davis recalls the town site of South Fort George. He notes it had a population by 1917 of only “about 300” and that the “boom was over”
Davis describes location of various businesses in South Fort George including the Rex Theatre, George St. Poole Room, McKay Bros. Grocery store, Drugstore, Bairds, Peters Butcher Shop.
Davis recalls that there were many “Yukoners” here at the time and recalls a tale about an old Yukoner
Mr. Davis recalls other people who worked on the BX with his father including Margaret “Granny” Seymour’s father;
Mr. Davis recalls riding up and down the river to Foley’s Cache on the sternwheeler as a child
Mr. Henry then speaks up and recalls trips on the sternwheeler with Arnold Davis on the boat as a child
Tape ends
Audio recording consists of individual taped interviews conducted by Bridget Moran with a number of early Fort George residents recalling the early years of white settlement in Prince George c.1910-c.1915. Interviews were conducted with the following individuals: Arnold Davis; J.A.F. Campbell; Alec Moffat; Claude Foot; George Henry; Nellie Law; John McInnis; Georgina [McInnis] Williams and Peter Wilson. These interviews were incorporated into the publication: Bridget Moran, Prince George Remembered…from Bridget Moran, Marsh Publishing, Prince George, 1996.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content:Recording consists of individual taped interviews conducted by Bridget Moran in a number of locations with Arnold Davis; J.A.F. Campbell; Alec Moffat; Claude Foot; George Henry; Nellie Law; John McInnis; Georgina [McInnis] Williams; Peter Wilson
Subjects include:
- Arnold Davis – former Sherriff in Prince George (born in 1882) arrived in Quesnel in 1909 and worked on the BX sternwheeler. Davis discusses his family roots from Ireland as a 6th generation Canadian. Recalls how his family arrived in South Fort George in 1917 and how his father worked on boats that went up and down Fraser River
- Claude Foot recalls coming from New Zealand to Fort George [Prince George] in 1906 and how there were ‘very few white men’; his father was Irish, mother was English
- Alex Moffat – describes how his parents provided a ‘stopping place’ for stage coaches in the Cariboo region
- George Henry recalls working on the boats that plied the Fraser River between Prince George and Soda Creek, near Quesnel
- Nellie Law – describes arriving from England in 1917 to Ashcroft and then Quesnel in 1917
- Peter Wilson – Barrister and Solicitor; the prosecutor for Prince George since 1916 describes arriving by train from Edmonton and arriving on a scow in South Fort George
- Mr. John McInnis – from Prince Edward Island, who sat twice in provincial legislature – in constituency of Grand Forks as socialist and later for constituency of Fort George recalls arriving in 1910 by rail to Kamloops and then by sleigh to South Fort George; describes the Indian Reserve at Fort George “[…don’t think there were a dozen white people…when I arrived […]”
- J.A. ‘Doc’ Campbell recalls being part of a survey crew in Fort George in 1908
- George Henry – also recalls cruising down the [Fraser] river by way of sternwheeler and losing men overboard
- Peter Wilson recalls experiences as practicing lawyer; there was no assize court in the region until 1919; recalls some of his early cases [murder case]
- Nellie Law describes working as a desk clerk at first The Alexandra Hotel and later The Prince George Hotel from 1918 to 1952
Law describes the hotel patrons and how she met the Duke and Duchess of Devonshire in 1922. Recalls stoking furnace with logs in the hotel to keep it warm and working as a bouncer - Alex Moffat – recalls workers and hauling freight via the old Cariboo Road; existence of one policeman only (BC Provincial Police); and describes in detail a stopping place for horses / crew on the Cariboo Road and the pack trains.
- Mr. Moffat – Describes the luxury experienced on the sternwheeler, The BX that “could carry seventy saloon passengers” and “staterooms were all equipped with push buttons, electric lights, hot and cold water, steam heat, and everything modern”
- Claude Foot – Recounts a dance in Quesnel at the hotel barroom and describes ordering drinks at the Al Johnson Hotel that had a bar which boasted to be “ the biggest bar in Canada, if not the world” 100 ft + bar with “six or seven bartenders behind this long bar, and the customers would be lined up two or three deep […]”
- J.A. [F.] [Campbell] – post-1910 changes with the use of scows on the Fraser River; describes the BC Provincial Police “in those days [they] just wore ordinary civilian clothes, but they were a tough bunch….[…]” and rowdiness in the bars in South Fort George
- Campbell describes the first bank in Fort George was the Bank of British North America that was housed in a tent and he recalls needing money while playing poker - ‘about eleven o’clock that night, the vault was open, and the till was open, and if you wanted money you’d walk up to the bank till and put an IOU in and take money out and go on playing [poker]
- Peter Wilson – comments about how lax the enforcement of law and order was in the early years including among the police themselves: “that the “Old Blind Nick [who] ran a bootlegging joint, went broke because he said he couldn’t afford to supply the police with any more liquor.”
- Claude Foot – recalls a fire in Quesnel in 1916 that burned a large part of the business section and the firemen were as Nellie Law notes “ a bucket brigade of Chinamen, filling buckets from a water hole in the Fraser River that the horses drank in…”
- John McInnis recalls political meetings and the election in 1916 when he was a candidate for the Fort George riding and being defeated by 7 votes; that the investigation of the election “was a whitewash”
- Georgina McInnis, who was the first White Child born in the community – she tells of the meeting that decided her name – as Fort Georgina McInnis
- Arnold Davis recalls his father working on boats that went up and down Fraser River and being on the boat with him and “watching the connecting rods go in and out and concentrate on pie…[served by the Chinese cook]” Davis also recalls The Yukoners who emigrated to PG after the Gold Rush
- George Henry recalls with lament the coming of the railway as he lost his job plying the River - preferred voyages on the Fraser River – and refers to those who worked the River and himself as “river rats”
Reel-to-reel audio recording consists of individual taped interviews conducted by Bridget Moran with a number of early Fort George residents recalling the early years of white settlement in Prince George c.1910-c.1915. Interviews were conducted with the following individuals: reel to reel recording of individual taped interviews and interview introductions by Bridget Moran with the following interviewees: Arnold Davis [former Sherriff for Prince George]; J.A.F. Campbell [PG land surveyor]; Alec Moffat; Claude Foot; Captain George Henry [sternboat captain]; Nellie Law [desk clerk at Alexandra and Prince George Hotel from 1918- 1952], John McInnis [former MLA for Fort George]; Georgina [McInnis] Williams; and Peter Wilson, [former Barrister and Solicitor and former Prosecutor for the City since its incorporation in 1915.] These interviews were incorporated into the publication: Bridget Moran, Prince George Remembered…from Bridget Moran, Marsh Publishing, Prince George, 1996.
Summary
Notes: Recording consists of individual taped interviews conducted by Bridget Moran and commentary by Moran that introduces each audio segment. Recording is exact copy of the written transcript later produced as the publication, Prince George Remembered…From Bridget Moran, Prince George: Marsh Publishing, 1996. In the publication foreword, Moran notes that she recorded the interviews on reels, then re-copied them on cassette tapes, and for the book project based on the recordings she did the edits and provided the introductory remarks for each interviewee’s audio segment.
See also the audiocassette summary for 2008.3.1.210.4 “History of Prince George”. The reel to reel recording is incomplete as it includes recorded interviews only for 61 minutes, not the full 80 minutes referred to in the audiocassette summary for 2008.3.1.210.4. The reel to reel recording continues only to the end of Claude Foot’s description of the bar at South Fort George [see transcript, Prince George Remembered… From Bridget Moran, p.25]
00’ 05”-5’00” Arnold Davis– talks about his family’s roots from Ireland and England and arriving in South Fort George in 1917;
5’10”-10’11” Claude Foot – talks about his family’s roots in New Zealand and memories of arriving in Quesnel in 1906, “very few white men”
10’12”-11’08” Alex Moffat – describes stage coach transportation throughout the Cariboo region
11’24”-12’33” George Henry describes working on the boats that plied the Fraser River with the BC Express Co.
13’17”-14’14” Nellie Law describes arriving in Quesnel from England in 1914 and later arriving in Prince George on the Fraser River in 1917. Law was the desk clerk at Alexandra and Prince George Hotel from 1918-1952.
14’45”-15’09” Peter Wilson describes arriving by work train to Prince George from McBride c.1915. Wilson was the Prosecutor for the City since its incorporation in 1915.
15’48”-20’02” Mr. John McInnis recalls arriving from Prince Edward Island in 1910 in Fort George due to the land prospecting for the town site. Describes 10 day horse & sleigh trip from Ashcroft to Fort George and briefly describes Indian Reserve in Fort George and recalls there were few white women in the town at that time.
20’25”-22’05” J.A. Campbell describes survey crew work he did at Fort George in 1908
22’16”-25’36” Captain George Henry recalls cruising down the Fraser River with a gas-powered boat c.1910 and losing crew overboard in the Fraser Canyon
25’47”-33’20” Peter Wilson recalls experiences as practicing lawyer and due to lack of assize court in Fort George until 1919 travelling to Clinton for court cases. Also describes difficulty of boat traveling to Peace River country to hear court cases there.
33’29”-39’24” Nellie Law recalls working first as a maid and then as a desk clerk with the Alexandra Hotel in 1919 and later the Prince George Hotel in 1923 – describes hotel guests; visit of Duke & Duchess of Devonshire; manual work performed including bouncing; stoking furnace in winter for heating.
39’45”-53’48” Alex Moffat – describes old Cariboo Road highway freighting and stage coach line at Barkerville and the ‘stopping places’ [roadhouses] on the Cariboo Road highway which his parents operated. Also describes Cataline’s pack train. Describes luxurious conditions on the BX sternwheeler boats.
56’10”-59’06” Claude Foot recounts a dance in Quesnel; card games and gambling at Barkerville 59’40”-1:00’58” Claude Foot recalls South Fort George and the ‘longest bar at South Fort George End of recording
End of recording
Photograph depicts large group posed on ceremonial steps in Agora courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Most individuals in group wear regalia. Bridget Moran stands in the second row, fifth from right (wearing sunglasses). Photo taken on the day Moran received an Honourary Law Degree.
Photograph depicts large group posed on ceremonial steps in Agora courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Most individuals in group wear regalia. Bridget Moran stands in the second row, fifth from right (wearing sunglasses). Other individuals can be seen standing around group. Photo taken on the day Moran received an Honourary Law Degree.
Photograph depicts large group posed on ceremonial steps in Agora courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Most individuals in group wear regalia. Bridget Moran appears to be standing in center of second row, hand raised to her face.
Photograph depicts large group posed on ceremonial steps in Agora courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Most individuals in group wear regalia. Bridget Moran stands in the second row, sixth from right (wearing sunglasses). Accompanying note from Maureen Faulkner: "Outside, the public photo session." Photo taken on the day Moran received an Honourary Law Degree.
Photograph depicts large group posed on ceremonial steps in Agora courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Most individuals in group wear regalia. Bridget Moran stands in the second row, sixth from right (wearing sunglasses). Photo taken on the day Moran received an Honourary Law Degree.
Photograph depicts two women, two men, a small child, and an infant on deck in backyard with chairs and table set with food and beverages. Trees and building visible in background. Accompanying note from Maureen Faulkner: "Ah ha! BBQ at M & T's." Photo taken on the day Bridget Moran received an Honourary Law Degree from the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C.
Photograph depicts grave marker which reads "ALLAN McCALLUM / 1906 - 1981 / RAISED NEAR HERE AS A SON OF A PIONEER FAMILY, HE WISHED TO BE RETURNED TO THIS PLACE HE LOVED ABOVE ALL OTHERS AND WHERE HE FELT SO AT PEACE."
Audio recording is of an interview by Bridget Moran with Margaret [Granny] Seymour at the PG Hospital in 1962. Moran later noted in another recording that the interview with Margaret Seymour was part of her social work. At the time of the interview Granny Seymour states she is 109 years old and says she is to celebrate her 110th birthday in June.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content:
- Talks about a flood in Fort George
- Went on a canoe from Fort St. James to Fort George
- Clothing and food that Granny Seymour grew up with
- Living at Fort St. James
- Discusses the poverty of the First Nations after moving to Shelley
- Discusses the priest who came to the reserve often
- Would cook dinner for the priest as often as she could
- Discusses memories of being a child and living in Fort St. James
- Traveling to Vancouver
- Police presence in Fort St. James – no police; She notes there was no police presence – the HBC boss provided policing. Recounts memories of one native at Ft St James who killed his boss
- Traveling to Fort Fraser by dog team
- Step dancing – remembers dances at Ft St James with the HBC crew
- Cleaning houses - Remembers taking care of house at Hudson’s Bay fort in Ft St James
- Health – talks about her health Visitors to Granny – Priest comes sometimes [to visit her now at the hospital]
- Did not go to school
- Discusses memories of her parents James Bouchey and her mother and her siblings
- Seymour’s first husband worked for HBC Ft St James was a white man Edward Flameau- unhappy memories of her marriage
- Seymour’s second husband was Billy Seymour – happier memories
- Getting caught in a forest fire and a big storm coming from Ft St James
- Talks about looking after Hudson’s Bay store and trading for sugar/tea
Tape ends
Audio recording is of an interview by Bridget Moran with Margaret [Granny] Seymour at the PG Hospital in 1962. Moran later noted in another recording that the interview with Margaret Seymour was part of her social work. At the time of the interview Granny Seymour states she is 109 years old and says she is to celebrate her 110th birthday in June.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content: Interview continues between Bridget Moran and Granny Seymour
- She talks about hard work that she performed at the [HBC] store
- Granny describes trapping at her own trap line
- Sometimes had more on her trap line than her husband had on his
- Talks about birth of her children at Hudson’s Bay in Ft St James and having to birth them on her own or with the help only of her sister [Nellie?] – as there was no doctor available
- Very skilled in medicine
- Everyone came to her for help
- Lived at Hudson’s Bay Post in Fort St. James
- Talks about employment
- Describes early South Fort George – when there were no houses at all; early residents including Charlie Ogmann [sp?]
- Granny notes her children never went to school but learnt quickly
- She learned how to speak French as her father was French
- Granny speaks about her mother – who is described as an “Indian Princess”
- Talks about husband Billy Seymour’s work; Granny describes building her own house at Fort George cutting and hauling down trees by hand
Tape ends
Photograph depicts Rex and Grace Boice sitting hand in hand and side by side in lawn chairs on patio. Flowers and hedges in background. Handwritten annotation on recto of photograph: "April 1993 Arizona. Rex died May 1, 1993 at home in Haliburton (heart attack). We celebrated our 34th wedding anniversary in March /93. We had a good Marriage! I miss him very much."
Photograph depicts two unidentified woman standing in front of tall plant in mall. Photo believed to have been taken in Newton, B.C.
Photograph depicts two horses in one of many fenced areas, buildings and machinery in background. Highway, house, and forest also visible in distance.
Photograph depicts men, women, and infant seated in the Canfor Theatre at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Unidentified individuals sit in seats in background. Accompanying note from Maureen Faulkner: "Next row down is R. [Roseanne Moran] & the Kennedy's, I move to join her next to walkway." Photo taken on the day Bridget Moran received an Honourary Law Degree.
Photograph depicts men, women, and infant sitting in crowded Canfor Theatre at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Accompanying note from Maureen Faulkner: "Your family. now behind R [Roseanne Moran] + me. look on with pride & interest." Photo taken on the day Bridget Moran received an Honourary Law Degree.
Polaroid photograph depicting large sanatorium building. Vehicles parked on street in foreground. Handwritten annotation on verso of photograph: "The Sanatorium. Fort Qu'Appelle - July 6/79".
Photograph depicts Millard seated on forest floor, with husky in foreground.
Photograph depicts dog seated on grass in foreground. Unidentified individuals visible below with fishing nets in waterfall area at Moricetown Canyon.
Photograph depicts couples dancing in large room, crowd seated on chairs against wall in background. Ornaments are hung in a row from ceiling. Man dancing in centre wears traditional dress. Handwritten annotation on recto of photograph: "Elders gathering 1983".
Photograph depicts landscape scene. Tree, bridge, and sign featuring cross country skier in foreground. Fence, hills, and forest in background.
Photograph depicts man and woman speculated to be Pat (Bridget Moran's son) and Tracy holding food and beverage on deck in backyard. Unidentified individuals semi-visible on far left and right. Trees and building visible in background. Photo taken on the day Bridget Moran received an Honourary Law Degree from the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C.
Photograph depicts many individuals wearing regalia, sitting in positions on convocation stage in Victoria, B.C. Bridget Moran sits between two men in front on right.
Photograph depicts Bridget Moran wearing University of Victoria regalia, seated at table with large book. Curtains hang in background, poinsettia plant sits on far right.
Photograph depicts Bridget Moran standing at podium on convocation stage in Victoria, B.C.
Photograph depicts Mary John seated to left of Moran at table in large room with tables, chairs, and couches. Skyscrapers visible through window in background. Accompanying note reads "Tea at the Empress! Feb/97"
Photograph depicts group of unidentified men and women seated in chairs in unknown classroom.
Photograph depicts Moran seated to left of two students presenting small knitted craft. Desk and chalkboard in background. Photograph was taken at session of Aboriginal Women's Training Program at the Cowichan Campus, Malaspina University College, in Duncan B.C. Handwritten annotation on recto of photograph: "Gifts from Charlene + Joanne Smith".
Item is a recording of an audio segment from CBC Radio in which CBC Reporter Karen Tankard provides a documentary report on the CBC Radio program Daybreak on conditions on the Stoney Creek reserve, outside of the farming community of Vanderhoof, 15 years after the inquest into Coreen Thomas’ death in Stoney Creek, BC. Tankard interviews community residents about the inquest and discusses the state of racism in the town of Vanderhoof, BC in 1991 and concludes improvements have not been made.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content: Tankard recalls that Maclean’s Magazine had written at the time of the inquest that “Vanderhoof was one of the most racially prejudiced towns in BC”
Tankard recalls Inquest of Coreen Gay Thomas’ death and includes archived interviews from the 1976 inquest. One Vanderhoof woman says people are putting “racial connotations’ around what is going on in Vanderhoof and that she has ‘many friendships’ with native people that ‘is not unusual’ While Minnie Thomas, a Band Councillor in 1976, discusses how poor white-native relations are on reserve and criticizes the state of housing and the economy on the Stoney Creek reserve
Tankard then talks to students at a dance on the reserve on Sept 15, 1991; she notes there is no high school for the native students. Native student Kevin Prince notes that “white kids don’t like native kids…”
Jackie Thomas who works at the Band Office states that the feelings of racism still exist here in 1991 Yet Vanderhoof Alderman Jack French states that he “doesn’t see it” in Vanderhoof now. Tankerd notes that Native people recall that the Inquest “shamed” the federal government into making some changes – some municipal services now exist and roads are paved in Stoney Creek, yet there is still 80% unemployment and a rise in drug and alcohol abuse. Gordon Smedley, editor of the Nechako newspaper discusses white-native relations 15 years after the inquest – and argues that a ‘core group’ of drug users impacts the image of natives in the community
Stoney Creek Elder Mary John argues that racism still exists and refers to how in the case of one native woman, who was a university graduate that she could not get even a clerical job in Vanderhoof
Vanderhoof resident Hugh Millard – argues that native residents from Stoney Creek are “not hampered by prejudice, but by a lack of education”
Bruce Smith, high school principal, expresses the challenges of keeping native kids in school; that activities have focused on liaison work with the Band. Smith notes the creation of the Yinka Dene Language Institute as means to keeping native students in school - seen as a ‘storefront’ school for adult education
Tankard notes RCMP also attempting to make changes and have hired a native constable
Yet Alderman Jack French notes there is not a lot of contact between the municipal council and the Stoney Creek Band Council – however argues that the municipality has avoided getting involved in such issues – “not our mandate” – the municipality’s mandate is to provide municipal services only.
Tankard recaps the findings of the Inquest – and questions if anything has really changed in Vanderhoof and Stoney Creek since the inquest.
While she recalls that Richard Redekopp was charged with criminal neglect that resulted in Thomas’ death – that due to a lack of evidence he was not convicted
Tankard surmises that perhaps the hope of the inquest that a reunion of white-native community in Vanderhoof and Stoney Creek was ‘too much’ and ‘unachievable’
End of documentary report by Karen Tankard
The Daybreak female radio broadcaster (unidentified) then invites Talk Back listeners to call in on the issue…..
End of tape
Audio cassette contains recorded audio interviews from a CBC Radio program interviewing Bridget Moran in the CBC Prince George studio on the recent publication of Justa.
Audiocassette Summary
Context: The recording is a segment from a CBC Radio program with broadcaster Mark [Forsythe?] interviewing Bridget Moran in the CBC Prince George studio on the recent publication of Justa. Mark first speaks to Justa by telephone asking him why he wanted his story told.
Scope and Content: Mark notes that Bridget Moran has just published a new book about the life of Justa Monk, entitled Justa: A First Nations Leader. Before speaking to Bridget, he speaks to Justa by telephone and asks him why he wanted his story told.
Justa says he wanted to tell people about the story of his life but also about the hardships of his people; for example he notes the transportation in the early years was difficult and that it took 21 hours by horse to travel from Tachie to Fort St. James. Also he says that what had happened to him [killing his brother] changed his life. He points out that in particular the Elders wanted him to tell his story. [Mark thanks Justa and the interview ends]
Mark then introduces Bridget Moran and asks her to comment on why she decided to write the book. Bridget first notes that she had heard about Justa’s life while writing the story of Mary John and that many people had suggested that she should write a book about his life as well. Although she had seen him at community events (potlatches) she was not introduced to him until November 1991. At that time he introduced himself and asked her to write his story – because he believed that it is possible to make amends for a bad life.
Bridget goes on to describe the circumstances leading to Justa killing his brother in a fight and that alcohol had been a factor. Justa had contemplated suicide.
Bridget then explains the setting of where Justa lived at Portage on Stuart Lake, 150 miles from Prince George. She notes that in many ways it was a very traditional life, totally dependent on the land. She says that Justa felt it was important in telling his story to tell native youth of ‘what they had – and what they had lost’.
Bridget then tells how Justa had been sent to a residential school at the age of 10 and that when he arriving the priest & nun took away his clothes. When he asks why – in Carrier – the only language he spoke – he was hit by the priest.
Bridget then talks about the structure of the book and notes that “what I was really doing was oral history.” She notes that she starting out interviewing him first because she notes she didn’t know him very well – but that it progress she then just talked with him. Bridget comments that Justa is a ‘real communicator’ and uses body language well – and she noted that he could remember details and emotions very well which gives a “sense of immediacy” to his story.
Mark asks Bridget to explain how Justa went from killing his brother – to becoming a leader of his people. Bridget notes that although it was felt he acted in self-defense, that Justa felt that he had to do penance for what he did. He was charged with manslaughter and served his time in a Forestry camp. After that he decided to go back to school and finish his education in Dawson Creek. He then decided to come back to Tachie to ‘make peace with his people’ and that the Elders forgave him and accepted him.
Justa then went on to work in the Band Office, then as Manager, then as Chief and in 1990 was elected as the Chief of the Carrier Sekani Tribal Council.
Bridget states that Justa’s legacy for native youth in particular – is that you can overcome hardships and turn your life around. Bridget notes that instead of drugs and alcohol that youths should look to their culture, language and Elders to help them.
Bridget then notes that her hope is to now hold workshops to help First Nations document their own history. To show them how they can take ‘raw material that I start work with’ and ‘work it up into a readable story.’ She hopes to hold workshops with Bands so that they can ‘do it for themselves’ – particularly as so many of the Elders are sick and dying and won’t be around to tell their stories.
Mark thanks Bridget –
End of interview
Audio cassette contains recorded audio interviews with Bridget Moran and Barbara Whittington on a CBC Radio program regarding the Judge Gove inquiry.
Audiocassette Summary
Context: The recording is a segment from a CBC Radio program with broadcaster Mark [Forsythe?] interviewing Barbara Whittington, professor of Social Work at the University of Victoria [on the telephone] and former social worker Bridget Moran on the telephone from Prince George. They are being interviewed about the recent report released by Judge Gove into the case of the death of a Metis child ‘Matthew’ [Vaudreuil]. The interview focuses on the need for reassessment of social workers and contract workers training and social work education in British Columbia to be coordinated by educators and the Ministry.
Scope and Content: Recording starts with interview in progress – Barbara is answering question by Mark on the findings of the Gove inquiry- that the judge captured the “sadness” of Matthews’ death in the report.
Bridget is then asked by Mark her views on the Inquiry’s report. She states that she didn’t have any problems with what the judge said – but that there is nothing experimental being done here. She notes however that no specific mention is made of the fact that Matthew was a Metis child in a poor family – and that this should have been addressed in the report and findings. Bridget refers to the fact that somehow ‘social workers got the wrong message’ – and refers to her work experience as a social worker that if children were seen at risk in a home then there were removed from their home.
Mark questions Barbara on how the inquiry may impact the teaching of social work. Barbara states she doesn’t’ think it will affect the teaching; and that the report had positive comments on the social work program at UVic – and refers to the working of a ‘decentralized model’ of work. However she notes that a Bachelor in Social Work needs to be seen as a ‘entry point’ only – and that comprehensive training between the University and Ministry [of Social Work] is needed.
Discussion of social worker salary; burnout; and the issue of utilizing contract workers is discussed. Bridget notes that she did some research into this 2 or 3 years ago – and that of the 2000-3000 social workers in BC – there was another 10,000 contract workers doing work ‘that don’t know what they’re doing’ – uneducated workers – dealing with the assessment of potential children at risk.
Barbara agrees that many are not well trained and not well supported and that a coordinated effort with the Ministry is needed so that burnout is addressed and that social workers get the support needed.
Barbara concludes that the report should have addressed the issue of contract workers more than it did. She also notes that it should have addressed the need for First Nations community training in social work
– and notes that there are many First Nations community members ‘ready to go’ with this training. Bridget agrees that this issue was not adequately addressed – and notes that about 60% of children in foster homes are aboriginal. She notes that if we ‘fail a person in one generation’ [as was Matthew’s mother] then we ‘fail children in the next generation’. Barbara agrees.
Mark thanks them both –
End of interview
Audio cassette contains recorded a audio segment from the CBC Radio program, Daybreak of broadcaster Alison Payne interviewing Bridget Moran on the recent publication of Stoney Creek Woman.
Audiocassette Summary
Context: The recording is a segment from the CBC Radio program, Daybreak of broadcaster Alison Payne interviewing Bridget Moran on the recent publication of Stoney Creek Woman.
Scope and Content: Alison asks Bridget to explain why she is labeled an ‘activist.’ Bridget recalls it comes from her public conflict as a social worker in 1964 when she criticized the WAC Bennett government of its lack of adequate services for foster children and welfare families. And that it was intensified by her open conflict in the BC Legislature in 1972 with the Minister of Welfare Phil Gaglardi, as Bridget, acting as a liaison for the Association of Social Workers and low income groups, criticized the government’s proposed passing of Bill 49 to amend the Social Assistance Act. (The Bill would, if passed, extinguish the right of appeal by welfare recipients if refused the right to services). Bridget recalls that because of the ‘noise in the gallery’ she made she was tossed out of the BC Legislature.
Alison asks Bridget about the book Stoney Creek Woman and why she felt the need to write it. Bridget explains she needed to write the book as she had felt ‘guilty’ about the plight of people on reserves her entire life – and refers to an incident in the 1950s when she had brought her mother Rose Anne Drugan to the Stoney Creek Reserve and revealed to her the plight of poor women on the reserve. Her mother made her promise to assist these women and Bridget states the book was a way to do this. The book about Mary John is a story of a “typical life” of people living on reserves. That it describes the nomadic lifestyle being changed to one of the ‘shock of the residential school’ and the ‘cultural genocide’ that followed. Bridget notes that it was Mary John who realized that Native People would need to speak for themselves to bring about social change.
Bridget speaks about her close relationship with Mary John; Bridget praises her work in trying to change the plight of her people on the reserve for the better and that it became a significant cause for Mary John after the death of Coreen Thomas. Bridget describes Mary John as a woman “dedicated to the world of emotions”
Alison notes at the end of the interview that the launch of the new book is to be held November 25, 1988 at Mosquito Books in Prince George.
End of interview
Item is a recording of an audio segment from CBC Radio in which a documentary update is provided on the inquest of Coreen Thomas.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content:
- Update on the case of deceased Coreen Gay Thomas
- July 3, 1976 Coreen Thomas is struck and killed by a car walking out to the Stoney Creek Reserve
- Police Report blamed Coreen for causing the accident saying that she was involved in a game of chicken
- The Driver of the car, Mr. Redekopp, had a high blood alcohol content but was not blamed for the crash
- Indians claimed that they were frequently harassed on the road by white motorists
- An inquest occurred and focused on relations between Indians and Whites
- Redekopp, coroner, police detachment, federal department of Indian affairs all seemed to be on trial
- Vanderhoof residents state media coverage is sensational with Vanderhoof unfairly labeled as “the most racially troubled town in Canada”
- Some see problem as due to lack of activities for young people in small communities
- Stoney Creek Indians live in intolerable conditions
- Interview with Stoney Creek Reserve resident regarding sanitation problems; lack of proper sewage system; cases of tuberculosis; high rate of unemployment; she states DIA should be responsible and should come up with a solution
- Problem with the perception of an alcoholic society;
- Archie Patrick, FN leader talks about the prejudice, harassment and racism found in Vanderhoof and other Northern communities towards Native People
- Good things could come out of this inquest – Vanderhoof residents should learn about poor living conditions at Stoney Creek
- Reporter provides update on the inquest; that local Police were accused of intimidating the witnesses
- Coreen Thomas’ death was unnatural but accidental
- Redekopp was negligible because vehicle was going too fast
- Segment of interview with Harry Rankin on the Thomas’ inquest; questions on the state of fairness of the inquest; and the state of white-native relations in northern BC
- Inquest Findings: Measures that should be put into place: Upgrade emergency system in the area, no person be placed in morgue before death certificate is in issue, get resident doctor for hospital, breathalyzers taken as soon as is legally permitted, RCMP officers be encouraged to have parent or guarding present when questioning young people as witnesses, Stoney Creek Band Council and Vanderhoof Council work to establish a Friendship Centre
Documentary ends with interview of Sophie Thomas on need for a change in white-native relations – and ends with excerpt of music from the Vanderhoof ‘pioneer’ song.
End of Tape
Audio recording is of an CKPG-CBC affiliate recording at the Supreme Court in Prince George regarding the 60th anniversary of Judge J.O. Wilson being called to bar.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content:
- CKPG-CBC affiliate recording at the Supreme Court in Prince George
- Justice Harold McInnis talks about Judge Wilson’s achievements and his career On the 60th Anniversary of his being called to the bar
- Other members of the Supreme Court congratulate him on his anniversary including Judge McInnis & Judge Stewart
- Judge Wilson recalls his early years practicing law
Water and opposite shore visible in background. Handwritten annotation on verso: "Miracle Beach - March 31/80".
Photograph depicts two large buildings across street in foreground, van visible on left.
Photograph depicts group of three at stone steps in courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia, in Prince George, B.C. Photo taken on the day Moran received an Honourary Law Degree. Left to right: Bob Harkins, Bridget Moran, unknown.
Audio cassette contains recorded audio interviews with Bridget Moran regarding Judgment at Stoney Creek with CBC/COOP/CKNW, 21-24 September 1990.
Audiocassette Summary
Scope and Content: CBC Radio Interview:
- CBC Radio Interviewer Bruce [last name?] introduces Bridget Moran who discusses her latest book Judgment at Stoney Creek, which describes the inquest into the death of Coreen Thomas, killed by a car driven by a drunk white man in 1976
- Moran discusses what she sees as “Third World conditions” experienced by Natives on reserves in Canada and discrimination against Native People by the Western justice system as experienced in the Thomas Inquiry in Vanderhoof
- Moran criticizes Prime Minster Brian Mulroney for the plight of Native Peoples in Canada; he had noted that the equivalent of $13,000.00 per year is spent on each Native person in Canada; Moran notes most Native people that she knows don’t see that money
- Moran notes that although she wrote Judgment at Stoney Creek in 1977, could not get it published as it was not considered “commercially viable”
- Bridget plans to write a book about her battle with the Social Credit Party
- Moran notes that this book comes out at a time [interview is during the Oka crisis] when Canadians have to be more aware of the need to settle land claim agreements with Native Peoples in BC and ensure that the environment is protected for the future; talks about massive logging and mineral prospecting occurring in BC which she notes concerns Stoney Creek Elders Mary John & Sophie Thomas
- Notes that few white people have been on reserves and have no contact with the Native way of life in Canada
Scope and Content: CKNW Radio Interview:
- CKNW Radio Interviewer Bill [Good?] introduces Moran and talks about the publication of the book. They discuss the status of native-white relations in BC both at the time of the Inquest into Coreen Thomas’ death and in 1990 at the time of the Oka crisis. Moran notes that natives in Canada don’t’ have the benefit of ‘the rule of law’ in Canada and experience injustice in the court system. Discusses the inquest; the role of Harry Rankin in the inquest. Moran concludes that only once Native People are involved in managing their own education, social welfare and political systems in Canada will conditions change.
Photograph depicts Rosanne standing with framed certificate in Agora courtyard at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, B.C. Unidentified individuals stand in background. Accompanying note from Maureen Faulkner: "R proudly displays your fine honors!."
Photograph depicts group of three in full regalia, sitting on stage at convocation ceremony in Victoria, B.C. Left to right: Richard Margison, Moran, unknown.
Photograph depicts close view of Moran wearing black shirt and colourful scarf, forest visible in background.
Photograph depicts close view of Moran wearing black shirt and colourful scarf, forest visible in background.
Photograph depicts close view of Moran wearing black shirt and colourful scarf, white wall in background.
Photograph depicts three women standing on beach in their Women's Royal Canadian Naval Service uniform. Waves and rocks in background. Handwritten annotation on recto of photograph: "Do you believe this?" Left to right: Bridget Moran, Betty Pincombe (aka 'Chick'), and Grace Boice (aka Tommy).
Photograph depicts three women sitting on beach in their Women's Royal Canadian Naval Service uniform. Purses and shoes lay beside them, large rock stands in background. Handwritten annotation on recto of photograph: "The California 'Beauties' 1946." Left to right: Betty Pincombe (aka 'Chick'), Bridget Moran, and Grace Boice (aka Tommy).